Effective patch management is a security cornerstone. Without timely security updates, your systems are sitting ducks for exploits. Automating your patch management process removes human error, boosts consistency, and gives you back your time — assuming you’re using the right tools. Let’s look at three of the best ways to automate patch management: PowerShell, WSUS, and PDQ Connect.
What is automated patch management?
Automated patch management uses tools or scripts to schedule, deploy, and verify software updates across all your endpoints — supporting vulnerability management and system security with no manual patching required. It cuts down on missed security patches, keeps compliance folks off your back, and frees you up for higher-level tasks (or at least for lunch).
How to automate patching with PowerShell
PowerShell’s no slouch when it comes to automated patch deployment. With the right scripts, you can automate the OS patching process — and even tackle third-party apps. But be ready to roll up your sleeves: You’ll need to track down updates, schedule them, and log them. It’s fully doable … assuming you have the time and the patience.
Step-by-step: Patch Windows with PowerShell
Scan for available updates
Start by loading up the Windows Update module (PSWindowsUpdate) to check what updates are waiting in the wings.Get-WindowsUpdateDownload and install updates
Want to install everything in one go without handholding? This’ll grab all available updates and reboot if needed:Install-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll -AutoRebootSchedule patching via Task Scheduler
Automated patching works best when you’re not awake to watch it. Set up a scheduled task to run your patching script during off-hours — like 3 a.m., when nothing’s running except your patch script (and that one mystery process that’s definitely not malware).Log results
Always log your installs. If something breaks later, you’ll want the receipts.
if(!(Test-Path 'C:\Logs')){
New-Item -Path 'C:\Logs' -ItemType Directory
}
$results = Install-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll -IgnoreReboot
$results | Out-File -FilePath "C:\Logs\PatchLog_$(Get-Date -Format 'yyyyMMdd').txt" Step-by-step: Patch third-party software with PowerShell
Find the silent installer URL
Head to the vendor’s site (like 7-Zip or Chrome), and grab the latest direct download link. Make sure it supports silent install switches (like/Sor/quiet).Download the installer
UseInvoke-WebRequestto pull the file to a local temp path. For example:$url = "https://www.7-zip.org/a/7z2301-x64.exe" $installer = "$env:TEMP\7z2301-x64.exe" Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $url -OutFile $installerRun the installer silently
Execute the installer with the appropriate silent flag:Start-Process -FilePath $installer -ArgumentList "/S" -WaitLog the installation result
Want to keep track of what got installed and when? Add a timestamped entry:if(!(Test-Path 'C:\Logs')){ New-Item -Path 'C:\Logs' -ItemType Directory } Add-Content "C:\Logs\PatchLog.txt" "$(Get-Date): 7-Zip installation completed."Repeat for each application
Each app needs its own mini-script. You can string them together in one master patch script or set them on their own timers using Task Scheduler. Your call.
PowerShell pros and cons
✅ Flexible and scriptable
✅ No third-party software required
❌ Requires careful error handling
❌ No built-in patch approval or compliance tracking
PowerShell is powerful but unforgiving. It’s great if you like writing and maintaining scripts — not so great if you need real-time visibility or reporting.
How to automate patching with WSUS
Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) is a long-standing solution for managing Microsoft updates in Windows environments.
Overview: Automate Windows patches using WSUS
Set up the WSUS server
Install the WSUS role and configure synchronization schedules.Approve updates
Choose which patches to approve for your environment — either manually or automatically based on classification.Configure Group Policy
Direct clients to the WSUS server using GPO settings.Set update timing
Use Group Policy to define when updates install and whether reboots are automatic.Monitor patch status
Check WSUS reports to track patch compliance and failures.
WSUS pros and cons
✅ Native Microsoft solution
✅ Centralized control for Windows updates
❌ No visibility into non-Windows software
❌ Clunky interface and limited control over deployment schedule
WSUS is decent for Microsoft-first shops, but it’s not exactly agile. For broader patch deployment needs, you’ll want something more modern.
How to automate patching with PDQ Connect
If you manage remote or hybrid machines, PDQ Connect can make your life easier. It’s a cloud-based patch manager that handles both Windows and third-party updates — no GPOs, VPNs, or script-wrangling required. You get real-time visibility, automatic retries if something fails, and a growing library of prebuilt packages that update as new versions come out.
Automate your patching
Keep devices patched and secure from the cloud.
Step-by-step: Automate patching with PDQ Connect
On the left navigation bar, select Automations. Click the Create automation button in the upper-right corner. For this example, I’ll focus on 7-Zip.
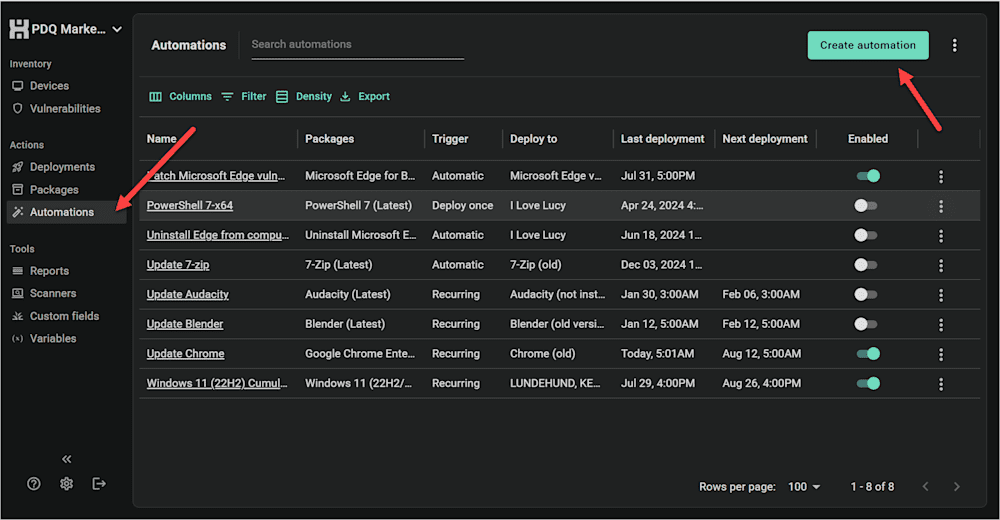
Name your automation and select the relevant package from our prebuilt Package Library, which includes more than 100 of the most popular apps. We update these when new versions are released to give you easy access to the latest updates and support true set-it-and-forget-it automation.

For the trigger, select Automatic to deploy updates as soon as a new version hits the Package Library. Alternatively, you can select Recurring if you prefer to update automatically on a set schedule. Finally, select the static or dynamic group you want to deploy patches to and click Save.
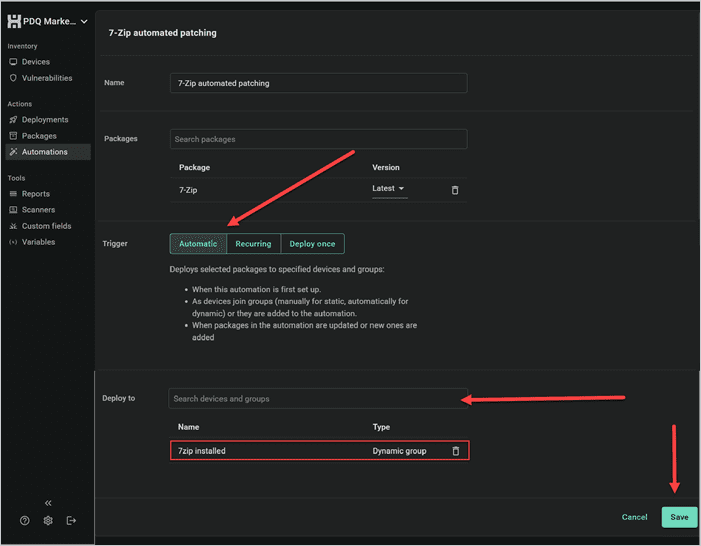
Easy peasy. Now I’ll never worry about 7-Zip falling out of date again. And once I repeat this process for the rest of the software in my environment, missing patches and unpatched software vulnerabilities will be a thing of the past. A few minutes now will prevent a lot of headaches later.
PDQ Connect pros and cons
✅ Cloud-native and built for remote teams
✅ Supports third-party and Windows updates
✅ Real-time feedback and retry logic
❌ Requires a subscription (but you can try it free for 14 days)
When to use which patch management method
Tool | Best for | Not ideal for |
PowerShell | Script-heavy orgs with in-house expertise | Non-scripting admins |
WSUS | On-prem shops with Microsoft-only stacks | Remote or hybrid environments |
PDQ Connect | Remote and multi-app environments | Air-gapped or completely offline sites |
Each method has its place, but for most modern IT teams, cloud-first automation like PDQ Connect offers the most flexibility with the least overhead.
Automated patch management FAQs
What is the difference between manual and automated patch management?
Manual patch management requires admins to identify, download, test, and deploy each update themselves — a time-consuming and error-prone process. Automated patch management solutions streamline this by handling patch discovery, deployment, and verification across endpoints on a schedule or trigger.
Why should I use an automated patch management tool?
An automated patch management tool helps enforce patch management policies, reduce human error, and ensure timely deployment of critical updates. These tools can improve security posture, increase uptime, and save IT teams hours of manual effort.
Can automated patch management handle third-party applications?
Yes, many automated patch management tools — like PDQ Connect and PDQ Deploy — support third-party patching. This includes deploying the latest patches without manual intervention.
How do I choose the right patch management solution?
Look for a patch management solution that fits your environment, including your OS mix and network setup. Most sysadmins prefer a tool that offers real-time visibility, automates critical patch deployment, supports compliance reporting, and plays nicely with their existing tools. Bonus points if it’s easy to use and scales with your organization.
Is automatic patching secure?
Yes, automatic patching is secure when properly configured. It ensures critical patches and security updates are applied promptly, reducing exposure to known vulnerabilities. However, you may want to test and vet packages before deployment to avoid disruption.
Automating patch management isn’t just a nice-to-have — it’s the only way to keep up. Whether you’re a PowerShell purist, a WSUS stalwart, or ready to embrace PDQ Connect, the key is consistency. Define your patch management policy, test patches, then let the automation do the heavy lifting.
Want to see what an automated patch management software like PDQ Connect can do for your patching strategy? Try it free for 14 days.