MSPs are now often expected to act as both IT support and cybersecurity providers. With attackers increasingly targeting managed service providers, consistency and automation are critical. These eight MSP cybersecurity best practices to know and implement for 2026 will help protect every client without overloading your team.
Watch the on-demand multitenancy webinar
See multitenancy in action in our on-demand webinar, Smarter Multitenancy and Simpler Security with PDQ Connect.
Why is cybersecurity consistency critical for MSP client protection?
When you manage dozens of client networks, consistency isn’t a luxury — it’s your only real defense. Every inconsistent patch policy or missed alert becomes a gap attackers can exploit. MSPs need standardized and auditable security workflows to ensure every client stays equally protected, regardless of size or complexity.
What are the top MSP cybersecurity best practices for 2026?
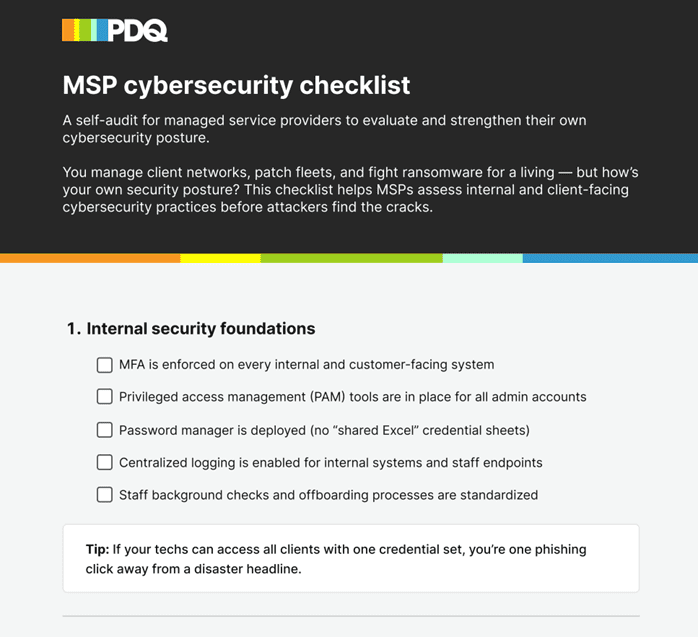
1. Internal security foundations
Internal MSP cybersecurity starts with your own environment. Enforce MFA, privilege controls, and secure offboarding to protect internal systems — and every client they touch.
Takeaway: Apply the same rigor to your internal environment that you expect from clients.
2. Endpoint and patch management
Automated patch management is essential for MSP security. Unpatched software is still a top attack vector, with an estimated one-third of ransomware attacks leveraging it. Use automation to ensure every endpoint — internal or client — is updated and reported consistently.
Takeaway: Use PDQ Connect’s remote patching and deployment features to automate updates and verify success without needing on-prem infrastructure.
Automate your patching
Keep devices patched and secure from the cloud.
3. Network and infrastructure hardening
MSP network security depends on strong segmentation and updated firewalls. To harden your infrastructure:
Audit VPNs and remote access.
Update and encrypt configuration backups.
Separate management and production networks.
Regularly patch firewalls, VPNs, and network appliances.
Takeaway: Treat your management network like production. Keep configurations encrypted and separated.
4. Cloud and SaaS security
Cloud and SaaS security for MSPs requires airtight configuration management. Even a single exposed admin token can compromise multiple clients. Enforce MFA, conditional access, credential hygiene, and the principle of least privilege across all platforms.
Takeaway: Review permissions and audit logs for every SaaS tool your team uses.
5. Monitoring and incident response
MSP incident response depends on continuous monitoring and alerting. You can’t fix what you can’t see — and you can’t respond to what you don’t detect. A clear plan separates secure MSPs from headlines.
Takeaway: Spot issues early with centralized visibility and rehearse like it’s real — because one day, it will be.
6. Staff training and culture
MSP security awareness starts with people, not firewalls. Build a security culture that treats awareness as a daily habit, not a checkbox. Regular cybersecurity training and phishing simulations reinforce that mindset.
Takeaway: Bake security into onboarding and run phishing simulations regularly.
7. Vendor and supply chain security
Vendor security for MSPs means verifying that every integration meets compliance and access standards. Audit API tokens and review vendor credentials regularly.
Takeaway: Protect your environment like it’s your crown jewel.
8. Backup and recovery
An MSP backup strategy should include immutable, offsite, encrypted, and versioned copies. Even the best defenses fail without tested backups, so recovery stays quick and reliable after a ransomware attack.
Takeaway: Backups should be automated, verified, isolated from production, and regularly tested.
MSP cybersecurity best practices FAQs
How do automation and centralized management improve MSP security?
Automation replaces guesswork with guarantees. Instead of manually pushing patches or juggling client portals, high-quality automation and reporting features let you manage everything from one secure console. That’s less busywork and fewer gaps.
What real results can MSPs expect from these best practices?
MSPs that standardize, automate, monitor, and report consistently reduce patch lag, improve compliance scores, boost client retention, and strengthen security posture.
How do MSPs build client trust with proactive security?
MSP cybersecurity isn’t just about preventing breaches — it’s about proving reliability. With PDQ Connect, MSPs can deliver consistent protection and keep every client secure, visible, compliant, and up to date — without building another on-prem fortress.
MSP cybersecurity success isn’t just about doing more — it’s about doing it consistently. Automate patching, standardize security workflows, maintain centralized visibility, and monitor everything from one place. PDQ Connect helps MSPs protect every client environment with the same speed and reliability. Sign up for a demo to see for yourself.